To make the wired LAN connection take priority you need to change the metric for the WIFI connection in the advanced settings pane of the WIFI connections' properties.
 Untick the 'Automatic metric' and set the metric to 9999 manually  Next open a commandline with admin rights and submit this command to clear the routing tables: route /fAfter this step reboot windows to make sure the new metric value gets used. Upon rebooting the routing tables will be rebuilt using ARP-discovery, causing the new metrics to be assigned to the routes. The net effect will be that to your TCP/IP stack it will look as if hosts/devices connected to the wired LAN have a more efficient route than those connecting via WIFI only. |
Tuesday, 6 January 2015
To make the wired LAN connection take priority you need to change the metric for the WIFI connection in the advanced settings pane of the WIFI connections' properties.
Thursday, 11 December 2014
Cannot disable User Account Control via control panel
Use this command in cmd
C:\Windows\System32\cmd.exe /k %windir%\System32\reg.exe ADD HKLM\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Policies\System /v EnableLUA /t REG_DWORD /d 0 /f
Tuesday, 9 December 2014
Microsoft Excel The file is corrupt and cannot be opened.
"The file is corrupt and cannot be opened" error on office 2010 Excel while opening .xls files

1. Open Excel 2010.
2. Click on File > Options.
3. Select Trust Center > Trust center settings.
4. Select Protected view.
5. Uncheck all the options under Protected View > OK.
6. Restart Excel 2010 and try to open Excel documents.
1. Open Excel 2010.
2. Click on File > Options.
3. Select Trust Center > Trust center settings.
4. Select Protected view.
5. Uncheck all the options under Protected View > OK.
6. Restart Excel 2010 and try to open Excel documents.
Thursday, 4 December 2014
SBS 2011/Server2008 Random reboots
Remote procedure call service crashes on a computer that is running Windows Server 2003 SP2, Windows Vista, Windows Server 2008, Windows 7 or Windows Server 2008 R
Follow this link
Symptoms
On a computer that is running Windows Server 2003 with Service Pack (SP2), Windows Vista, Windows Server 2008, Windows 7 or Windows Server 2008 R2, a Svchost.exe process that hosts the remote procedure call (RPC) service crashes. When this issue occurs, the following error message is logged in the Application log:
Event Type: Error
Event Source: Application Event Category: None Event ID: 1000 Date: <date> Time: <time> User: N/A Computer: <computer> Description: Faulting application svchost.exe version <version>, faulting module rpcrt4.dll, version <version>, fault address <address>. Cause
This error occurs because the remote procedure call service does not wait for all the asynchronous RPC calls to be returned before the service reallocates the structure. Because of this behavior, the asynchronous RPC calls access an incorrect reallocated address. Therefore, an access violation occurs, and the RPC service crashes.
ResolutionHotfix informationA supported hotfix is available from Microsoft. However, this hotfix is intended to correct only the problem that is described in this article. Apply this hotfix only to systems that are experiencing the problem described in this article. This hotfix might receive additional testing. Therefore, if you are not severely affected by this problem, we recommend that you wait for the next software update that contains this hotfix.If the hotfix is available for download, there is a "Hotfix download available" section at the top of this Knowledge Base article. If this section does not appear, contact Microsoft Customer Service and Support to obtain the hotfix. |
Thursday, 27 November 2014
How To Segment A Small LAN Using Tagged VLANs
Ask Tech Support Specialists Now
How To Segment A Small LAN Using Tagged VLANs
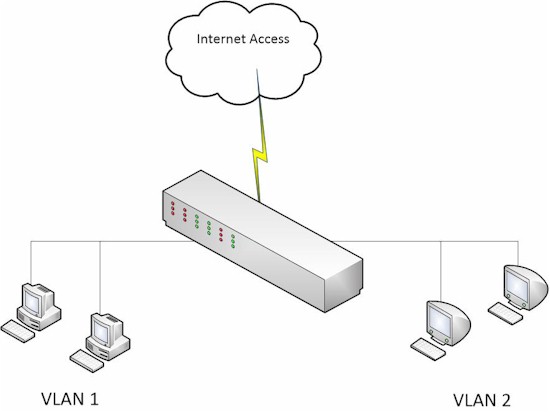
Introduction
VLANs, or Virtual LANs, are a useful technology for segmenting a network. I covered some VLAN basics awhile back in this article. Implementing VLANs in a small network can be simple or tricky, depending on the VLAN capabilities of your switch and router. For example, what should you do if you want to use VLANs with a VLAN-capable switch, but your router doesn't support VLANs?Example 1: Port-based VLAN switch
Let's say you have a VLAN-capable "smart" switch, but your router doesn't support VLANs. Your goal is to segment traffic on the switch in multiple VLANs to prevent devices on one VLAN from accessing devices in the other VLAN, but allow all devices to access the Internet. A simple solution is to set up port-based VLANs on the switch.Start by enabling port-based VLANs and creating three VLANs on the switch. VLAN 1 will be for the internet, VLAN 2 will be for one set of devices and VLAN 3 will be for another set of devices. Below shows a NETGEAR GS108Tv1 enabled for port-based VLANs with VLANs 1-3 created.
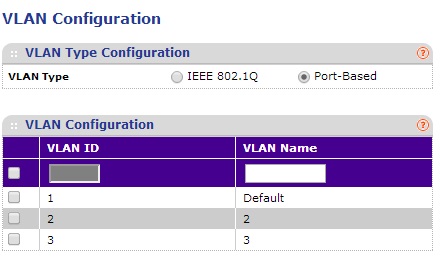
NETGEAR GS108Tv1 Enable Port-Based VLAN
Next, assign VLANs to the appropriate ports. Assign VLAN 1 to port 1 and connect your router to port 1 on the switch. Now assign VLAN 2 to ports 1 and 2. Finally, assign VLAN 3 to ports1 and 3.In the screenshots below from a NETGEAR GS108Tv1, port 1 is a member of VLANs 1, 2, and 3. Port 2 is a member of only VLAN 2. Port 3 is a member of only VLAN 3. To add more devices to one of the VLANs, simply add their ports to either VLAN 2 or VLAN 3.
NETGEAR GS108Tv1 Port-Based VLAN Assignments
The end result of this example is devices in VLAN 2 can access the Internet and each other and devices in VLAN 3 can access the Internet and each other. But devices in VLAN 2 cannot access devices in VLAN 3 and vice versa.Example 2: 802.1Q Switch
Let's say you have a switch supporting 802.1Q VLANs, but not port-based VLANs, the same no-VLAN router and want to segment traffic as you did in Example 1.It's helpful to clarify some terms first. 802.1Q, sometimes referred to as VLAN tagging, is a standard technology that defines how data traffic is tagged with a VLAN ID. Tagging traffic with a VLAN ID allows the traffic to remain a member of a VLAN as it is passed from one port to another, or from one device to another. 802.1Q specifies that all traffic is tagged with a VLAN ID, except traffic on the port's native VLAN. A port's native VLAN is also known as the the PVID, or Port VLAN Identifier.
802.1Q VLANs can have different port types. An access port is an 802.1Q VLAN port that can be assigned to a single VLAN only. It is typically used to connect to end devices such as PCs. A trunk port is an 802.1Q VLAN port that can carry traffic for multiple VLANs and is typically used to interconnect 802.1Q VLAN capable switches and routers. Some switches use general ports, which are a hybrid between access and trunk ports and can carry traffic for multiple VLANs.
To implement the Example 1 solution using 802.1Q VLAN technology, enable 802.1Q on the switch and create the three VLANs as you did in the port-based VLAN example. In this example, I'm going to again use a NETGEAR GS108Tv1, which supports both port-based and 802.1Q VLANs. The below configurations will also work on many NETGEAR switches, including a NETGEAR GS108Tv2. As you can see below, I've enabled 802.1Q and created VLANs 1-3.
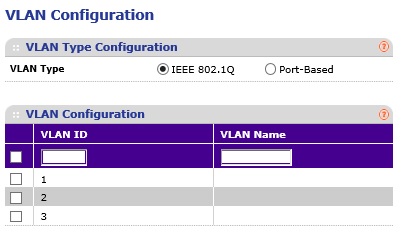
NETGEAR GS108Tv1 Enable 802.1Q VLANs
Then, if your switch allows for setting VLAN port type to access, trunk, or general, set the ports to general. Some switches, such as the NETGEAR GS108Tv1 and NETGEAR GS108Tv2 (and most NETGEAR switches I've reviewed,) allow all ports to be members of multiple 802.1Q VLANs so you don't have to set VLAN port type. Other switches, such as the Cisco SG200-26, which I'll cover in the last example, require you to change the VLAN port type to general for this kind of configuration.Next, assign VLANs to the appropriate ports with the untagged designation, which is a "U" on the NETGEAR GS108Tv1, and make all ports untagged members of VLAN 1. Then make ports for one set of devices untagged members of VLAN 2 and set ports for the other set of devices untagged members of VLAN 3. As you can see in the composite image below from a NETGEAR GS108Tv1, all ports are untagged members of VLAN 1, ports 1 and 2 are untagged members of VLAN 2, and ports 1 and 3 are untagged members of VLAN 3.
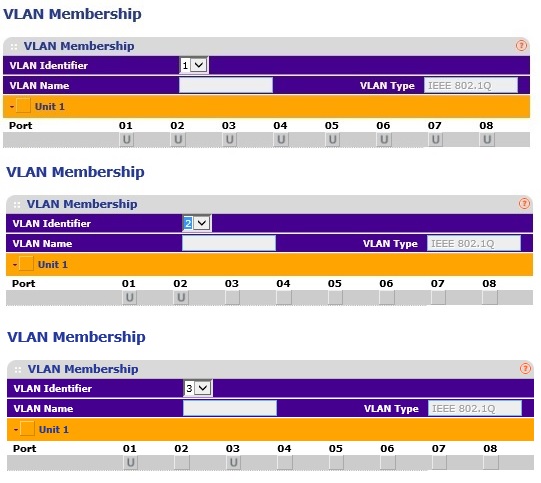
NETGEAR GS108Tv1 802.1Q VLAN Assignments
The last step is to set the PVIDs. Set the PVID on the port connected to the router as VLAN 1. Set the PVID on the ports for one set of devices to VLAN 2. Set the PVID for the ports for the other set of devices to VLAN 3. Below is a screen shot of the NETGEAR GS108Tv1 PVID settings.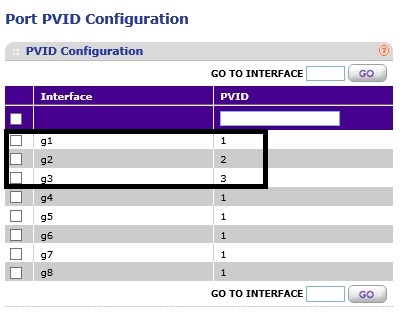
NETGEAR GS108Tv1 802.1Q PVID Assignments
With this configuration, the device connected to port 2 can't access the device connected to port 3 and vice-versa. But both devices have internet access. To add more devices, configure their ports as untagged members of VLAN 2 or VLAN 3 and make their PVID either VLAN 2 or VLAN 3.How To Segment A Small LAN Using Tagged VLANs - Example 3, Example 4, Closing
Example 3: ZyXEL GS1900-8HP
In the above two examples, I used VLANs 1-3. You can use any VLANs you want, as long as you have the port configurations correct.Here's a configuration summary of the following screenshots:
- VLAN 2 = Internet, VLAN 3 = PC 1, VLAN 4 = PC 2.
- Port 6 is connected to my router. Port 6 is an untagged member of VLAN 2, 3, and 4 with a PVID of 2.
- Port 7 is connected to PC 1. Port 7 is an untagged member of VLAN 2 and 3 with a PVID of 3.
- Port 8 is connected to PC 2. Port 8 is an untagged member of VLAN 2 and 4 with a PVID of 4.
Zyxel GS1900-8HP 802.1Q VLAN Assignments
...the second screen shot shows the PVID configuration.Zyxel GS1900-8HP 802.1Q PVID Assignments
With this configuration, PC 1 and PC 2 can access the Internet but not each other. To add another device in the same VLAN as PC 1 or PC 2, configure the port as an untagged member of VLAN 2 and an untagged member of either VLAN 3 or 4, plus set the PVID to either VLAN 3 or 4.Example 4: Cisco SG200-26
To perform the same configurations on a Cisco SG200-26 switch, which only supports 802.1Q, the approach is similar to Example 3. Simply create the desired VLANs, configure the interfaces as general and make all interfaces untagged members of the Internet VLAN. Then assign the appropriate interfaces as untagged members of their desired VLAN and, finally, assign PVIDs.The screenshot below shows the VLAN port-types, VLAN assignments, and PVID assignments on the Cisco SG200-26. Notice in the Mode column that all three interfaces are configured as "General." I used VLAN 4 for the Internet and VLANs 51 and 52 for PCs. A "U" after the VLAN ID indicates untagged, and a "P" after a VLAN ID indicates PVID.
Here's a config summary of the below screenshot:
- Interface GE10 is connected to PC 1. Interface GE10 is an untagged member of VLAN 4 and 51 with a PVID of 51.
- Interface GE11 is connected to PC 2. Interface GE11 is an untagged member of VLAN 4 and 52 with a PVID of 52.
- Interface GE12 is connected to my router. Interface GE12 is an untagged member of VLAN 4, 51 and 52 with a PVID of 4.
Cisco SG200-26 802.1Q Configuration
With this configuration, PC 1 and PC 2 can access the Internet but not each other. To add another device in the same VLAN as PC 1 or PC 2, configure the switch interface as general, make it an untagged member of VLAN 4 and an untagged member of either VLAN 51 or 52 and set the interface PVID to either VLAN 51 or 52.While this example was done on a Cisco SG200-26, the Cisco SG200-08 and SG200-08P use similar configurations.
Closing
In all the examples, all end devices are in the same IP address range (subnet) and the router doesn't support VLANs. It is also interesting to note in Examples 2-4 using 802.1Q VLANs, we don't actually use tagging, since we set all ports to be untagged members of the various VLANs.If you look closely at the VLAN assignments in the port-based and 802.1Q examples, you can see that the router/Internet port is a member of all VLANs for both port-based and 802.1Q. The difference is the PC ports are members of only one VLAN in a port-based config, whereas PC ports are members of the Internet VLAN and their native VLAN in an 802.1Q config.
These examples are limited to segmenting a wired network using VLANs only on ports of a smart / managed switch. In a future article, I'll cover how to use 802.1Q VLANs using ports on both a router and switch, as well as how to use 802.1Q VLANs to segment a wireless network.
Below is a table of switches I've used or reviewed that lists whether they support port-based and/or 802.1Q VLANs.
| Switch | Port-Based | 802.1Q |
|---|---|---|
| Cisco SG200-26 | N | Y |
| Cisco SG500-28P | N | Y |
| HP PS1810 | Y | Y |
| LG-Ericsson ES-2026 | Y | Y |
| NETGEAR GS108Tv1 | Y | Y |
| NETGEAR GS108Tv2 | N | Y |
| NETGEAR GS510TP | N | Y |
| NETGEAR GS716T | N | Y |
| NETGEAR GS724TR | N | Y |
| NETGEAR M4100 | N | Y |
| TRENDnet TEG160WS | N | Y |
| TP-LINK TL-SG108E | Y | Y |
| TP-LINK TL-SG2008 | N | Y |
| TP-LINK TL-SG2216 | N | Y |
| ZyXEL GS1900-8HP | N | Y |
On the other hand, 802.1Q is a standard technology that is supported by most VLAN-capable switches. The bottom line, as shown in these examples, is you can use port-based or 802.1Q VLANs to segment any small network.
Wednesday, 19 November 2014
How To Fix ERROR_NOT_FOUND 0x80070490 During Windows 7 SP1 Installation
How To Fix ERROR_NOT_FOUND 0x80070490 During Windows 7 SP1 Installation
 Well, this one took ages. And whenever something takes me ages, rather than write it down in my personal notes, I prefer to put it out online for everyone with the same problem to easily find and benefit from.
Well, this one took ages. And whenever something takes me ages, rather than write it down in my personal notes, I prefer to put it out online for everyone with the same problem to easily find and benefit from.The problem I'm talking about today is trying to upgrade your Windows 7 installation to SP1 by applying Microsoft's update KB976932, called "Windows 7 Service Pack 1 for x64-based Systems" and getting nothing but a failure every time. The same problem may affect 32-bit systems as well, and I'm not sure what the update number for that would be, but the solution should work for either one.
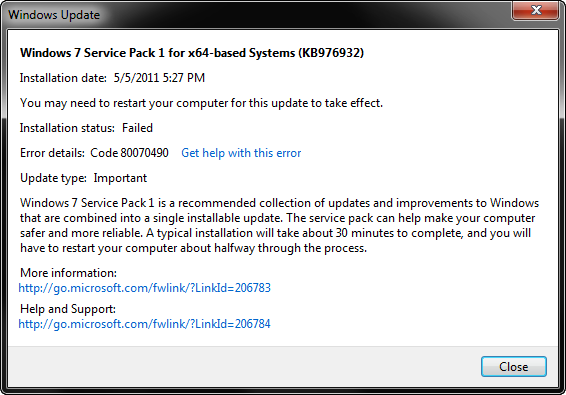
The update starts just fine, chugs along for 10 minutes or so, then reboots the system and starts performing more operations, when suddenly one of them fails about 10% down the road, reboots, and reverts the whole process. You end up with this message (code 80070490) and a failure for which there are a lot of useless "solutions" on the web that just don't work.
Except for one. I can't take credit for it – all I did was spend a month weeding through the crap, retrying, and getting nowhere, until a genius by the name Ben-IS came up with exactly the right diagnosis and provided exactly the right solution. This solution, in my own interpretation, is below.
Step 1
We are going to use a utility called SFC (System File Checker or Windows Resource Checker), which is part of the Windows installation. It will help diagnose the problem.Open up a command prompt (cmd) as administrator and run
sfc /scannowThis will run for a while and produce a file called CBS.log which you can find in %WINDIR%\Logs\CBS (usually C:\Windows\Logs\CBS). See this KB929833 for more info on SFC and CBS (Component Based Servicing).
sfc /scannowEven though there are no integrity violations, we should have enough info in the log to diagnose the problem.
Beginning system scan. This process will take some time.
Beginning verification phase of system scan.
Verification 100% complete.
Windows Resource Protection did not find any integrity violations.
Step 2
Unfortunately, Windows overwrote my CBS.log, so I'll go by the one Ben-IS provided.Open up CBS.log and look for something like Failed uninstalling driver updates or 0x80070490 – ERROR_NOT_FOUND.
If you have this line, which you should if you're reading this post, you should also see lines similar to these a few lines above:
2011-04-14 12:02:33, Info CBS Doqe: q-uninstall: Inf: usbvideo.inf, Ranking: 2, Device-Install: 0, Key: 598, Identity: usbvideo.inf, Culture=neutral, Type=driverUpdate, Version=6.1.7600.16543, PublicKeyToken=31bf3856ad364e35, ProcessorArchitecture=amd64, versionScope=NonSxSOne of these .inf files is the culprit, and we're going to find out which one in the next step.
2011-04-14 12:02:33, Info CBS Doqe: q-uninstall: Inf: sffdisk.inf, Ranking: 2, Device-Install: 0, Key: 599, Identity: sffdisk.inf, Culture=neutral, Type=driverUpdate, Version=6.1.7600.16438, PublicKeyToken=31bf3856ad364e35, ProcessorArchitecture=amd64, versionScope=NonSxS
2011-04-14 12:02:33, Info CBS Doqe: q-uninstall: Inf: sdbus.inf, Ranking: 2, Device-Install: 0, Key: 600, Identity: sdbus.inf, Culture=neutral, Type=driverUpdate, Version=6.1.7600.16438, PublicKeyToken=31bf3856ad364e35, ProcessorArchitecture=amd64, versionScope=NonSxS
Step 3
Now open up a different log file located at %WINDIR%\inf\setupapi.dev.log (normally c:\Windows\inf\setupapi.dev.log).Look for a line that contains Failed to find driver update or FAILURE(0x00000490).
Note the exact path to the .inf file that failed. In my case, it was:
sto: Failed to find driver update 'C:\Windows\WinSxS\amd64_usbvideo.inf_31bf3856ad364e35_6.1.7600.16543_none_8a1a2513d42628c3\usbvideo.inf' in Driver Store. Error = 0x00000490
Step 4
This is the key to the whole operation. Open up the command prompt again (cmd) as administrator and runpnputil -a INSERT_FILE_NAME_FROM_STEP_3For example, I ran
pnputil -a C:\Windows\WinSxS\amd64_usbvideo.inf_31bf3856ad364e35_6.1.7600.16543_none_8a1a2513d42628c3\usbvideo.infYou should see the following dialog:
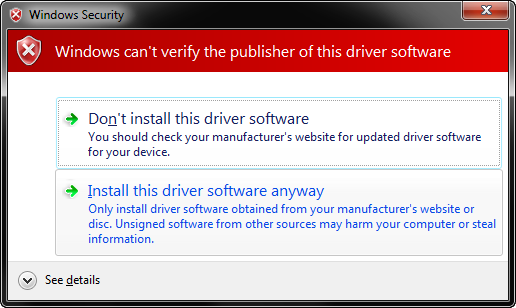
Choose Install this driver software anyway.
The end result should be something like this:
pnputil -a C:\Windows\WinSxS\amd64_usbvideo.inf_31bf3856ad364e35_6.1.7600.16543_none_8a1a2513d42628c3\usbvideo.infRepeat this step for any failures found in step 3.
Microsoft PnP Utility
Processing inf : usbvideo.inf
Driver package added successfully.
Published name : oem69.inf
Total attempted: 1
Number successfully imported: 1
Step 5
Apply the SP1 Windows Update again – it should now install successfully.And voila – enjoy your SP1!
Thursday, 13 November 2014
Win 8.1 Pastel no companies showing up
on windows 8.1, we must change the permissions in the registry to full control to add the companies in pastel
Hkey_Current _User \Software\Classes\VirtualStore\Machine\Software\Wow6432node\Softline\pastel V12
If encounter the problem
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)




